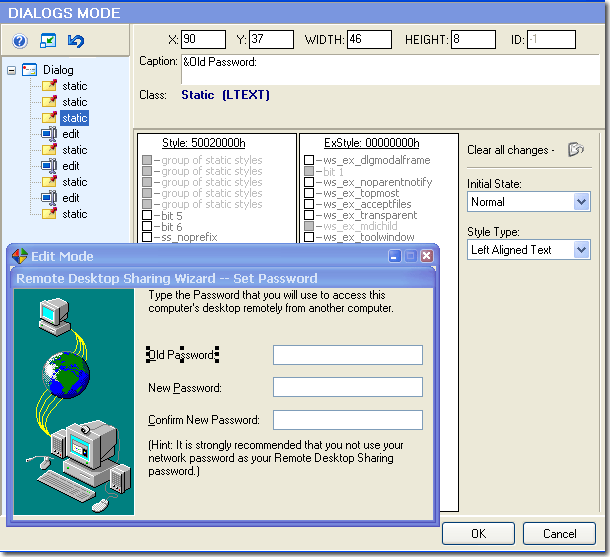
Dialog edit mode lets you visually modify a selected dialog and its controls.
You can resize, redesign, and reposition dialogs or simply change their font
properties to suit your wishes.
However, Windows® imposes restrictions on changes that can be made. These
limitations are described in Important
Notes.
Size and position changes to dialog boxes and child controls are automatically
reflected in the resource script.
For more information see: DIALOG
Resource.
1. Select the dialog resource item to be changed in the Resource Tree
view.
2. Open the dialog resource using the "Resource Editor" button
 or the popup menu displayed by
right-clicking the Resource Tree. Or simply double-click the resource item directly.
or the popup menu displayed by
right-clicking the Resource Tree. Or simply double-click the resource item directly.
3. Select a control by clicking it in the displayed dialog. The selected
control will show resizing handles.
4. A dialog box can be modified primarily by editing the item lable -
e.g. the caption, as well as changing the size or position of a control. This
can be accomplished using the mouse as well as entering the new properties directly
into the corresponding edit fields.
5. Press OK to close the Resource Editor and select 'File' -> 'Save
File As ...' to save the altered file to disk. If warned that the image size
has changed, click "Yes" to update the file size.
Control IDs can not be edited. These values are hard coded into the target
file. Changing them is likely to cause the modified program to crash.
 Show/Hide a dialog
form.
Show/Hide a dialog
form.
 Change font properties
of a dialog form (when selecting a dialog node).
Change font properties
of a dialog form (when selecting a dialog node).
 Rollback. There
are two rollback buttons: Total rollback
Rollback. There
are two rollback buttons: Total rollback  restores all changes, Local rollback
restores all changes, Local rollback  restores only changes made to a selected control.
restores only changes made to a selected control.
Any change you make can be restored prior to quitting the editor using the OK
button. To abort your changes quit the editor using the Cancel button.
STYLE PARAMETERS
This menu allows for changing the Style and ExStyle parameters of a selected
control:

You can set/reset the extended style parameters for a dialog box and its control
items (e.g. "right-to-left" reading order for Hebrew/Arabic script
as well as "right-aligned text").
For more information regarding the various extended styles, see CONTROL
CLASSES AND STYLES.

